When rainy days cause your shoulders and ankles to ache again, when you discover a leg injury after finishing a soccer game, or when you find yourself unable to straighten your back after a week of desk work, your friends might suggest using ice and heat treatment. But can heat treatment and ice treatment be used together?
While both heat treatment and ice treatment are crucial for the recovery of wounds and bodily areas, how should we choose the appropriate pain relief treatment based on different scenarios?
First, let's understand what ice treatment and heat treatment are.
HOW DOES ICE TREATMENT WORK?
Ice treatment is a physical treatment that uses low temperatures (0°C–10°C) to treat injuries. Its core principle is to use low temperatures to constrict blood vessels, reduce bleeding and tissue fluid leakage in the affected area, inhibit nerve pain transmission, thereby lowering pain sensitivity, and reduce cellular metabolic rates to quickly control acute inflammatory responses.
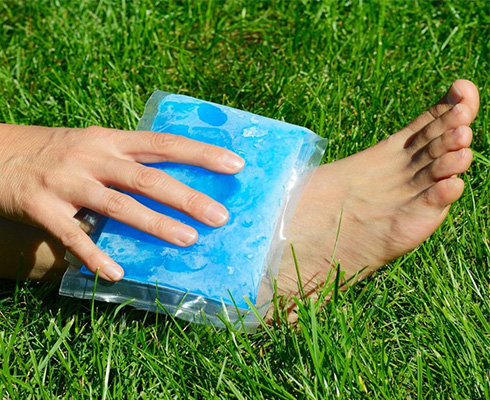


TYPES OF ICE TREATMENT:
Ice treatment is most commonly used in the early stages of acute injuries, such as ankle sprains, muscle strains, and other common sports-related injuries. Applying an ice pack for continuous ice treatment within 20 hours can effectively reduce swelling by over 30%. However, if the injured area is a pre-existing injury, we do not recommend continuous ice application before exercise or competition, as this can significantly impair performance.
You can make an ice pack by placing ice cubes in a plastic bag and wrapping it in a towel, or use disposable ice packs available on the market. Apply the ice pack directly to the injury to relieve pain, but be sure not to exceed 20 minutes of ice treatment, as this can cause frostbite!
HOW DOES HEAT TREATMENT WORKS?
Heat treatment is a physical treatment method that uses thermal energy (typically 40–45°C) to act on human tissues, causing local capillary dilation. By promoting blood circulation, increasing oxygen and nutrient delivery, it alleviates pain and accelerates tissue repair. Its core principle involves using thermal stimulation to dilate blood vessels, enhance metabolic rate, strengthen cellular repair capabilities, and inhibit pain nerve transmission.
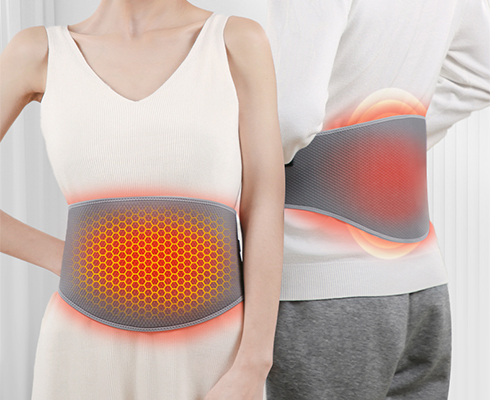
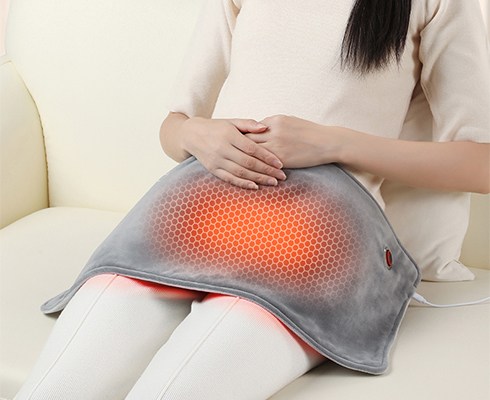

Types of heat treatment:
Thermal treatment is commonly used for chronic pain and muscle strain, such as arthritis, shoulder inflammation, lower back strain, cervical spondylosis, and more. Current far-infrared heating treatment technology is highly mature and widely applied, such as microwave heat treatment in hospitals, infrared chambers, precise heating of tumor sites, and palliative care for advanced cancer patients, as well as immune function regulation. For home use, we recommend graphene-heated therapeutic devices such as heated blankets, heated knee supports, and heated neck supports. Each use should not exceed 20-30 minutes, and the temperature should not exceed 45°C during continuous use to prevent low-temperature burns. Note that heat treatment products should not be used for acute muscle strains or sprains, as this may exacerbate pain and swelling in the affected area.
In summary, we can see that ice treatment is effective for acute sports injuries, while heat treatment is more suitable for long-term body aches or muscle strain.
♦ If you notice swelling in your knees or ankles, we strongly recommend using ice packs for relief. However, please note that each application should not exceed 15 minutes. To enhance the effectiveness of ice treatment, you can elevate the injured area appropriately.
♦ If you experience chronic pain in certain body parts due to prolonged sitting or old injuries, especially during rainy or humid weather, graphene heat treatment is the optimal solution. Graphene heat treatment belts and knee guards help relax muscles, improve blood circulation, and alleviate pain.
Please consider discontinuing the use of pain medications, as prolonged use of any medication can be a burden on the body. For those with chronic conditions, we strongly encourage you to explore the benefits of heat treatment!